Tibetan Spaniel Joint Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction
Overview of Tibetan Spaniel: The Tibetan Spaniel, often affectionately called the “Tibbie,” is a small, charming breed with a rich history dating back over 2,000 years. Originating from the mountainous regions of Tibet, these dogs were bred by Buddhist monks to serve as companions and watchdogs in monasteries. Known for their intelligence, independence, and affectionate nature, Tibetan Spaniels are characterized by their distinctive lion-like mane, expressive eyes, and a plumed tail that curls over their back. Despite their small size, they possess a sturdy and well-balanced build.
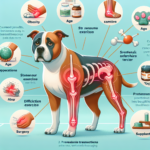
General Health Concerns: Like many purebred dogs, Tibetan Spaniels are prone to certain health issues. Common concerns include progressive retinal atrophy (PRA), patellar luxation, and respiratory problems due to their brachycephalic (short-nosed) structure. Among these, joint pain is a significant issue that can affect their quality of life.
Importance of Joint Health in Tibetan Spaniels: Joint health is crucial for Tibetan Spaniels due to their active and playful nature. Healthy joints allow them to move freely, engage in physical activities, and maintain their overall well-being. Joint pain can severely limit their mobility, leading to a sedentary lifestyle, which can further exacerbate other health problems.
Breed-Specific Joint Pain Risks
Genetic Predisposition
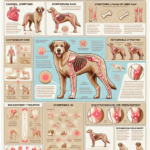
Tibetan Spaniels have a genetic predisposition to several joint-related issues. Hip dysplasia, a condition where the hip joint doesn’t fit properly into the hip socket, is relatively common. This can lead to arthritis and chronic pain. Elbow dysplasia, although less common, can also occur. These genetic factors make it essential for breeders to screen for joint issues and for owners to be vigilant about their dog’s joint health.
Age-Related Risks
As Tibetan Spaniels age, the risk of developing joint pain increases. Degenerative joint diseases like osteoarthritis are more likely to manifest in older dogs. Typically, signs of joint pain may start appearing around middle age, which for Tibetan Spaniels is around 6-8 years. However, some dogs may show symptoms earlier, especially if they have a genetic predisposition or have experienced joint injuries.
Activity Level and Joint Stress
Tibetan Spaniels are moderately active dogs that enjoy playtime and short walks. However, their small size and relatively delicate joints mean that excessive or high-impact activities can lead to joint stress. Activities like jumping from heights, running on hard surfaces, or engaging in strenuous exercise can contribute to joint wear and tear over time.
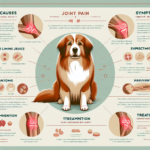
Common Symptoms of Joint Pain in Tibetan Spaniels
General Symptoms
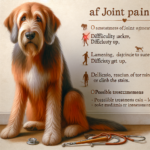
Owners should be aware of the following common symptoms of joint pain in Tibetan Spaniels:
- Limping: A noticeable limp or favoring one leg over another.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in getting up or lying down, especially after rest.
- Reluctance to Move: Hesitation or refusal to climb stairs, jump, or engage in physical activities.
- Swelling: Visible swelling around the joints.
- Behavioral Changes: Increased irritability or signs of discomfort when touched.
Breed-Specific Symptoms
In Tibetan Spaniels, joint pain may also manifest as a reluctance to perform their characteristic “watchdog” duties, such as perching on high surfaces to observe their surroundings. They may also show a decreased interest in play and social interactions, which is unusual for this typically sociable breed.
When to Consult a Vet
If you notice any of the above symptoms, it is crucial to consult a veterinarian promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life for your Tibetan Spaniel. Persistent limping, severe stiffness, or any signs of pain should not be ignored.
Preventive Measures for Joint Health
Exercise Recommendations
Maintaining an appropriate exercise routine is vital for the joint health of Tibetan Spaniels. Low-impact activities such as short walks, gentle play sessions, and swimming are excellent choices. Avoid high-impact exercises like jumping or running on hard surfaces. Regular, moderate exercise helps keep the joints flexible and muscles strong, which supports joint health.
Dietary Suggestions
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for joint health. Consider incorporating the following into your Tibetan Spaniel’s diet:
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These supplements support cartilage health and joint function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, these have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint pain.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing joint stress. Obesity can exacerbate joint pain and lead to other health issues. Monitor your Tibetan Spaniel’s weight and adjust their diet and exercise routine as needed to keep them at an optimal weight.
Early Screening and Monitoring
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for early detection of joint issues. Screening tests such as X-rays or joint fluid analysis can help identify problems before they become severe. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and slow the progression of joint diseases.
Treatment Options for Joint Pain
Non-Surgical Treatments
Several non-surgical treatments can help manage joint pain in Tibetan Spaniels:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. Always consult your vet before administering any medication.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and therapies designed to improve joint function and reduce pain can be highly effective.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Modifying your dog’s activity level and providing a comfortable living environment can help manage pain.
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common surgical options include:
- Joint Replacement: Replacing a damaged joint with an artificial one can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to clean out the joint and remove damaged tissue.
- Osteotomy: Cutting and realigning bones to improve joint function.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative treatments can also be beneficial for managing joint pain:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Hydrotherapy: Water-based exercises that reduce joint stress while improving strength and flexibility.
- Massage: Regular massages can help reduce muscle tension and improve circulation.
Lifestyle and Management Tips
Daily Care Routine
A sample daily care routine for managing joint pain in Tibetan Spaniels might include:
- Morning: Gentle walk followed by a joint supplement with breakfast.
- Midday: Short play session with low-impact toys.
- Afternoon: Another gentle walk or hydrotherapy session.
- Evening: Massage and relaxation time on an orthopedic bed.
Modifying the Home Environment
Making your home more comfortable for a dog with joint pain can significantly improve their quality of life. Consider the following modifications:
- Ramps: Use ramps instead of stairs to reduce joint stress.
- Orthopedic Beds: Provide a supportive bed to alleviate pressure on joints.
- Non-Slip Flooring: Ensure floors are non-slip to prevent falls and injuries.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management strategies include regular veterinary check-ups, consistent exercise, a balanced diet, and ongoing monitoring of your dog’s condition. Adjustments to their care routine may be necessary as they age or if their condition changes.
FAQs About Tibetan Spaniels and Joint Pain
What are the early signs of joint pain in Tibetan Spaniels?
Early signs include limping, stiffness, reluctance to move, and behavioral changes such as irritability or decreased interest in play.
Can joint pain in Tibetan Spaniels be prevented?
While genetic predispositions cannot be entirely prevented, maintaining a healthy weight, providing appropriate exercise, and regular veterinary check-ups can help reduce the risk and severity of joint pain.
Are there specific foods that can help with joint health?
Yes, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, chondroitin, and antioxidants can support joint health. Consult your vet for specific dietary recommendations.
When should I consider surgery for my dog’s joint pain?
Surgery should be considered when non-surgical treatments are no longer effective, and your dog’s quality of life is significantly impacted. Consult your veterinarian for a thorough evaluation and recommendation.
Conclusion
Joint pain is a significant concern for Tibetan Spaniels, but with proper care and attention, it can be managed effectively. By understanding the causes, symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment options, owners can ensure their Tibetan Spaniels lead happy, active lives. Regular veterinary consultations and a proactive approach to joint health are essential for maintaining your dog’s well-being. Remember, early intervention and consistent care can make a world of difference in your Tibetan Spaniel’s quality of life.