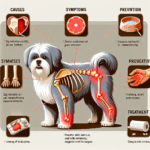
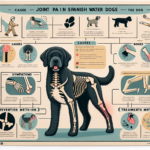
Spanish Water Dog Joint Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction
The Spanish Water Dog (SWD) is a versatile and intelligent breed known for its curly coat and exceptional working abilities. Originating from Spain, this breed has a rich history of herding, hunting, and even performing water rescues. With a medium build and a robust, athletic physique, the Spanish Water Dog is both a loyal companion and a diligent worker. However, like many breeds, the SWD is prone to certain health issues, including joint pain, which can significantly impact their quality of life.
General Health Concerns
While the Spanish Water Dog is generally a healthy breed, they are susceptible to several health issues, including hip dysplasia, progressive retinal atrophy (PRA), and hypothyroidism. Among these, joint pain is a particularly concerning issue that can affect their mobility and overall well-being.
Importance of Joint Health in Spanish Water Dogs
Joint health is crucial for the Spanish Water Dog due to their active lifestyle and working nature. Whether they are herding livestock, participating in agility sports, or simply enjoying a vigorous play session, healthy joints are essential for their performance and happiness. Neglecting joint health can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and a diminished quality of life.
Breed-Specific Joint Pain Risks
Genetic Predisposition
The Spanish Water Dog is genetically predisposed to several joint-related issues, most notably hip dysplasia and elbow dysplasia. Hip dysplasia occurs when the hip joint does not fit properly into the hip socket, leading to pain and arthritis over time. Elbow dysplasia involves abnormal development of the elbow joint, which can also result in pain and lameness. Both conditions are hereditary and can be exacerbated by environmental factors.
Age-Related Risks
As Spanish Water Dogs age, the risk of developing joint pain increases. Older dogs are more likely to suffer from arthritis, a degenerative joint disease that causes inflammation and pain. For this breed, significant age milestones to watch for include the onset of middle age (around 5-7 years) and senior years (10 years and older). Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for early detection and management of age-related joint issues.
Activity Level and Joint Stress
The Spanish Water Dog is known for its high energy levels and active lifestyle. While regular exercise is beneficial for overall health, excessive or inappropriate activity can put undue stress on their joints. Activities such as jumping, running on hard surfaces, or intense agility training can contribute to joint wear and tear. It’s important to balance their need for exercise with activities that are gentle on the joints.
Common Symptoms of Joint Pain in Spanish Water Dogs
General Symptoms
Owners should be vigilant for common symptoms of joint pain, which include:
- Limping or favoring one leg
- Stiffness, especially after rest or sleep
- Reluctance to climb stairs or jump
- Decreased activity or playfulness
- Visible discomfort or pain when touched
- Swelling around the joints
Breed-Specific Symptoms
In Spanish Water Dogs, joint pain may manifest in specific ways due to their unique build and activity levels. For instance, they may show a noticeable decrease in their enthusiasm for water activities or herding tasks. Additionally, their curly coat can sometimes obscure swelling or changes in muscle mass, making it essential for owners to perform regular, thorough checks.
When to Consult a Vet
If you notice any of the above symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a veterinarian promptly. Early intervention can prevent further deterioration and improve your dog’s quality of life. Persistent limping, severe pain, or any sudden changes in behavior warrant immediate veterinary attention.
Preventive Measures for Joint Health
Exercise Recommendations
Maintaining an appropriate exercise regimen is key to preserving joint health in Spanish Water Dogs. Low-impact activities such as swimming, walking on soft surfaces, and controlled play sessions are ideal. Avoid high-impact exercises like jumping or running on hard surfaces, which can exacerbate joint stress. Regular, moderate exercise helps maintain muscle mass and joint flexibility.
Dietary Suggestions
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall health and joint function. Consider incorporating foods or supplements that contain:
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These compounds help maintain cartilage health and reduce inflammation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, these fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate joint pain.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E can help reduce oxidative stress on joints.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing joint stress. Excess weight puts additional pressure on the joints, exacerbating pain and accelerating degeneration. Regularly monitor your dog’s weight and adjust their diet and exercise routine as needed to keep them within a healthy range.
Early Screening and Monitoring
Early detection of joint issues can significantly improve outcomes. Regular veterinary check-ups should include screenings for joint health, especially as your dog ages. Genetic testing for predispositions to conditions like hip and elbow dysplasia can also inform preventive strategies.
Treatment Options for Joint Pain
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense against joint pain. These may include:
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and inflammation. Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin can also be beneficial.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises designed to strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility can alleviate pain.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Modifying your dog’s activity level and providing a comfortable living environment can make a significant difference.
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common surgical options include:
- Hip Replacement: This procedure involves replacing the damaged hip joint with an artificial one.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgery used to diagnose and treat joint issues.
- Osteotomy: This surgery involves cutting and realigning bones to relieve joint stress.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative treatments can complement traditional methods and provide additional relief. These may include:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
- Hydrotherapy: Water-based exercises are gentle on the joints and can improve mobility.
- Massage Therapy: Regular massages can alleviate muscle tension and improve circulation.
Lifestyle and Management Tips
Daily Care Routine
A consistent daily care routine can help manage joint pain effectively. This might include:
- Morning and evening walks on soft surfaces
- Regular, gentle stretching exercises
- Administering prescribed medications or supplements
- Providing a balanced diet with joint-supporting nutrients
Modifying the Home Environment
Making your home more comfortable for a dog with joint pain can significantly improve their quality of life. Consider:
- Installing ramps to help them navigate stairs
- Providing orthopedic beds for better joint support
- Using non-slip mats to prevent falls
- Ensuring food and water bowls are at a comfortable height
Long-Term Management
Long-term management strategies are essential for keeping your Spanish Water Dog active and happy despite joint pain. Regular veterinary check-ups, consistent exercise, and a supportive home environment are key components. Additionally, staying informed about new treatments and therapies can provide ongoing relief and improve your dog’s quality of life.
FAQs About Spanish Water Dogs and Joint Pain
What are the early signs of joint pain in Spanish Water Dogs?
Early signs include limping, stiffness, reluctance to move, and decreased activity levels. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your veterinarian for a thorough evaluation.
Can joint pain in Spanish Water Dogs be prevented?
While genetic predispositions cannot be entirely prevented, maintaining a healthy weight, providing appropriate exercise, and regular veterinary check-ups can significantly reduce the risk and severity of joint pain.
Are there specific foods that can help with joint health?
Yes, foods rich in glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids can support joint health. Consult your veterinarian for dietary recommendations tailored to your dog’s needs.
Is surgery always necessary for joint pain?
No, surgery is usually considered a last resort. Many cases of joint pain can be managed effectively with non-surgical treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
How often should I take my Spanish Water Dog to the vet for joint health check-ups?
Regular check-ups are essential, especially as your dog ages. Annual visits are recommended for younger dogs, while bi-annual visits may be necessary for older dogs or those showing signs of joint pain.
Conclusion
Joint pain is a significant concern for Spanish Water Dogs, but with proper care and preventive measures, it can be managed effectively. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight management, and early screening are crucial for maintaining joint health. If joint pain does occur, a range of treatment options, from medications to alternative therapies, can provide relief. By staying vigilant and proactive, you can ensure your Spanish Water Dog enjoys a happy, active life.
Remember, always consult your veterinarian for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your dog’s specific needs.