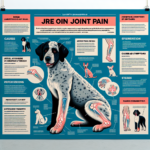
Jindo Joint Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction
The Jindo, also known as the Korean Jindo Dog, is a breed that hails from Jindo Island in South Korea. Renowned for their loyalty, intelligence, and hunting prowess, Jindos have a rich history that dates back several centuries. They are medium-sized dogs with a well-proportioned, muscular build, and a double coat that can be either short or long. Their keen senses and strong territorial instincts make them excellent guard dogs and companions.
Like many breeds, Jindos are susceptible to certain health issues, with joint pain being a significant concern. Joint health is crucial for maintaining the overall well-being and quality of life for Jindos, as it directly impacts their mobility and ability to engage in daily activities.
Breed-Specific Joint Pain Risks
Genetic Predisposition
Jindos, like many other breeds, can be genetically predisposed to joint-related issues. Common conditions include hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, and arthritis. Hip dysplasia is a malformation of the hip joint that can lead to arthritis and pain, while elbow dysplasia involves abnormal development of the elbow joint. Both conditions can significantly impair a Jindo’s mobility and quality of life.
Age-Related Risks
As Jindos age, the risk of developing joint pain increases. Typically, signs of joint issues may start to appear in middle age, around 5 to 7 years old. However, some dogs may show symptoms earlier or later, depending on their genetic makeup and lifestyle. It’s essential for owners to be vigilant and monitor their Jindo’s joint health as they age.
Activity Level and Joint Stress
Jindos are known for their high energy levels and need for regular exercise. While this activity is beneficial for their overall health, it can also contribute to joint stress, especially if the dog engages in high-impact activities like jumping or running on hard surfaces. Owners should be mindful of the types of activities their Jindo participates in to minimize joint strain.
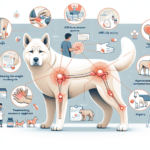
Common Symptoms of Joint Pain in Jindos
General Symptoms
- Limping or favoring one leg
- Stiffness, especially after resting
- Reluctance to move or climb stairs
- Decreased activity or playfulness
- Visible discomfort or pain when touched
Breed-Specific Symptoms
In Jindos, joint pain may manifest as a reluctance to engage in activities they once enjoyed, such as running or playing fetch. They may also show signs of discomfort when getting up from a lying position or exhibit a noticeable change in their gait.
When to Consult a Vet
If you notice any of the above symptoms in your Jindo, it’s crucial to consult a veterinarian promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life for your dog. Regular veterinary check-ups are also essential for monitoring joint health and catching any issues early.
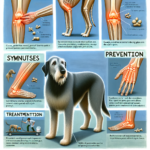
Preventive Measures for Joint Health
Exercise Recommendations
Regular, low-impact exercise is vital for maintaining joint health in Jindos. Activities such as walking, swimming, and controlled play can help keep their joints flexible and muscles strong without causing excessive strain. Avoid high-impact activities like jumping or running on hard surfaces, which can exacerbate joint issues.
Dietary Suggestions
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support joint health. Look for dog foods that contain glucosamine and chondroitin, which are known to promote joint health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, can also help reduce inflammation and support joint function.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing joint stress. Excess weight can put additional pressure on the joints, exacerbating pain and discomfort. Monitor your Jindo’s weight and adjust their diet and exercise routine as needed to keep them at an optimal weight.
Early Screening and Monitoring
Regular veterinary check-ups and early screening for joint issues can help catch problems before they become severe. Your vet may recommend X-rays or other diagnostic tests to assess your Jindo’s joint health and provide appropriate interventions if needed.
Treatment Options for Joint Pain
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments for joint pain in Jindos include medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy and hydrotherapy can also be beneficial in improving joint mobility and strength. Lifestyle adjustments, such as providing a comfortable bed and avoiding high-impact activities, can further alleviate joint pain.
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common surgeries for joint issues include hip replacement, arthroscopy, and joint fusion. These procedures can significantly improve a Jindo’s quality of life, but they come with risks and require a thorough discussion with your veterinarian.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative treatments such as acupuncture, massage, and laser therapy can provide additional relief for joint pain. These therapies can help reduce inflammation, improve circulation, and promote healing. Always consult with your veterinarian before starting any alternative treatments to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your Jindo.
Lifestyle and Management Tips
Daily Care Routine
A consistent daily care routine can help manage and alleviate joint pain in Jindos. This routine might include gentle exercise, a balanced diet, and regular use of joint supplements. Monitoring your dog’s behavior and adjusting their activities as needed can also help manage pain.
Modifying the Home Environment
Making your home more comfortable for a Jindo with joint pain can significantly improve their quality of life. Consider adding ramps to help them navigate stairs, providing orthopedic beds for better support, and using non-slip mats to prevent falls on slippery surfaces.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management of joint pain involves regular veterinary check-ups, ongoing use of medications or supplements, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Keeping your Jindo active and engaged with low-impact activities can help them stay happy and healthy despite joint pain.
FAQs About Jindos and Joint Pain
What are the early signs of joint pain in Jindos?
Early signs of joint pain in Jindos include limping, stiffness, reluctance to move, and decreased activity levels. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your veterinarian for a thorough evaluation.
Can joint pain in Jindos be prevented?
While genetic predisposition cannot be changed, you can take preventive measures to reduce the risk of joint pain. These include maintaining a healthy weight, providing regular low-impact exercise, and ensuring a balanced diet rich in joint-supporting nutrients.
Are there specific exercises that are better for Jindos with joint pain?
Yes, low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and controlled play are ideal for Jindos with joint pain. These activities help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength without causing excessive strain.
What dietary supplements can help with joint health in Jindos?
Supplements containing glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids can support joint health in Jindos. Always consult your veterinarian before starting any new supplements to ensure they are appropriate for your dog.
When should I consider surgery for my Jindo’s joint pain?
Surgery should be considered when non-surgical treatments are no longer effective, and your Jindo’s quality of life is significantly impacted. Discuss the potential benefits and risks with your veterinarian to make an informed decision.
Conclusion
Joint pain is a common concern for Jindos, but with proper care and preventive measures, you can help your dog maintain a healthy and active life. Regular veterinary check-ups, a balanced diet, appropriate exercise, and early intervention are key to managing joint health. By staying vigilant and proactive, you can ensure your Jindo enjoys a high quality of life for years to come.