German Shepherd Dog Joint Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction
German Shepherd Dogs (GSDs) are one of the most popular and recognizable dog breeds in the world. Originating from Germany in the late 19th century, they were initially bred for herding and guarding sheep. Over time, their intelligence, strength, and versatility have made them ideal for various roles, including police and military work, search and rescue, and as loyal family pets. German Shepherds are known for their courage, loyalty, and keen sense of duty, making them a beloved breed among dog enthusiasts.
Despite their many admirable qualities, German Shepherds are prone to several health issues, with joint pain being one of the most significant concerns. Joint pain in German Shepherds can stem from various causes, including genetic predispositions, age-related wear and tear, and the physical demands of their active lifestyles. Understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of joint pain in German Shepherds is crucial for ensuring their long-term health and well-being.
Joint health is particularly important for German Shepherds due to their active nature and the physical demands placed on their bodies. Maintaining healthy joints can help prevent pain and mobility issues, allowing these dogs to lead active, fulfilling lives. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of joint pain in German Shepherds, including the risks, symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment options available.
Breed-Specific Joint Pain Risks
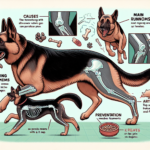
Genetic Predisposition
German Shepherds are genetically predisposed to several joint-related issues, including hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, and arthritis. Hip dysplasia is a condition where the hip joint does not fit properly into the hip socket, leading to pain and eventual arthritis. Elbow dysplasia involves abnormal development of the elbow joint, causing lameness and discomfort. These conditions are often hereditary, meaning that they can be passed down from one generation to the next.
Age-Related Risks
As German Shepherds age, they become more susceptible to joint pain and related issues. The breed typically reaches senior status around seven years of age, at which point the wear and tear on their joints can become more pronounced. Age-related joint pain can manifest as osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that causes the cartilage in the joints to break down, leading to pain and stiffness.
Activity Level and Joint Stress
German Shepherds are known for their high energy levels and need for regular physical activity. While exercise is essential for their overall health, excessive or inappropriate activity can place undue stress on their joints. Activities such as running, jumping, and playing on hard surfaces can exacerbate joint issues, especially if the dog is already predisposed to conditions like hip or elbow dysplasia.
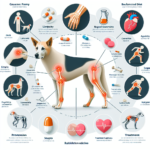
Common Symptoms of Joint Pain in German Shepherds
General Symptoms
Owners should be vigilant for common symptoms of joint pain in their German Shepherds, including:
- Limping or favoring one leg
- Stiffness, especially after rest or exercise
- Reluctance to move, jump, or climb stairs
- Decreased activity or playfulness
- Swelling or heat around the joints
- Whining or showing signs of discomfort when touched
Breed-Specific Symptoms
In German Shepherds, certain symptoms may be more pronounced due to their size and activity level. For example, they may exhibit a noticeable “bunny hopping” gait when running, which can indicate hip dysplasia. Additionally, they may show a reluctance to perform tasks that were previously easy for them, such as jumping into a car or climbing stairs.
When to Consult a Vet
If you notice any of the above symptoms in your German Shepherd, it is essential to consult a veterinarian promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage joint pain and prevent further deterioration. A veterinarian can perform a thorough examination, including X-rays or other imaging tests, to determine the underlying cause of the joint pain and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Preventive Measures for Joint Health
Exercise Recommendations
Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining joint health in German Shepherds, but it is essential to choose the right types of activities. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and controlled play are ideal for keeping their joints healthy without causing excessive stress. Avoid activities that involve repetitive jumping or running on hard surfaces, as these can exacerbate joint issues.
Dietary Suggestions
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support joint health in German Shepherds. Consider incorporating foods or supplements that contain glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids, as these can help maintain cartilage health and reduce inflammation. Consult your veterinarian for specific dietary recommendations tailored to your dog’s needs.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing joint stress in German Shepherds. Excess weight can place additional pressure on the joints, exacerbating pain and discomfort. Monitor your dog’s weight regularly and adjust their diet and exercise routine as needed to keep them at an optimal weight. Your veterinarian can provide guidance on appropriate weight management strategies for your dog.
Early Screening and Monitoring
Early screening and monitoring can help detect joint issues before they become severe. Regular veterinary check-ups, including orthopedic evaluations, can identify potential problems early on. For German Shepherds, it is advisable to have hip and elbow evaluations performed by a veterinarian experienced in diagnosing joint conditions. Early intervention can help manage joint pain and improve your dog’s quality of life.
Treatment Options for Joint Pain
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatment options for joint pain in German Shepherds include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. Your veterinarian may also prescribe pain relievers or joint supplements.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can improve joint mobility and strengthen the muscles around the joints. Techniques such as hydrotherapy, massage, and controlled exercises can be beneficial.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Modifying your dog’s activity level and providing a comfortable living environment can help manage joint pain. Avoid high-impact activities and provide supportive bedding.
Surgical Options
In severe cases of joint pain, surgical intervention may be necessary. Common surgical options for German Shepherds include:
- Hip Replacement: Total hip replacement involves replacing the damaged hip joint with an artificial one. This surgery can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Elbow Surgery: Procedures such as arthroscopy or corrective osteotomy can address elbow dysplasia and improve joint function.
- Arthrodesis: This procedure involves fusing the joint to eliminate pain and stabilize the affected area.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies can complement traditional treatments and provide additional relief for joint pain. Some options include:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture can help reduce pain and inflammation by stimulating specific points on the body.
- Hydrotherapy: Water-based exercises can improve joint mobility and reduce pain without placing stress on the joints.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help relax muscles, improve circulation, and alleviate joint pain.
Lifestyle and Management Tips
Daily Care Routine
A consistent daily care routine can help manage and alleviate joint pain in German Shepherds. Consider the following tips:
- Provide regular, low-impact exercise to maintain joint mobility.
- Incorporate joint supplements into your dog’s diet as recommended by your veterinarian.
- Monitor your dog’s weight and adjust their diet and exercise routine as needed.
- Schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor joint health and address any issues promptly.
Modifying the Home Environment
Making your home more comfortable for a dog with joint pain can significantly improve their quality of life. Consider the following modifications:
- Provide orthopedic beds to support your dog’s joints while they rest.
- Use ramps or steps to help your dog access furniture or vehicles without jumping.
- Place non-slip mats on slippery surfaces to prevent falls and injuries.
- Ensure that food and water bowls are at a comfortable height to reduce strain on the neck and joints.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management strategies can help keep your German Shepherd active and happy despite joint pain. Consider the following approaches:
- Maintain a consistent exercise routine that includes low-impact activities.
- Continue providing joint supplements and a balanced diet to support joint health.
- Monitor your dog’s weight and make adjustments as needed to prevent excess strain on the joints.
- Stay in regular communication with your veterinarian to address any changes in your dog’s condition and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
FAQs About German Shepherds and Joint Pain
What are the early signs of joint pain in German Shepherds?
Early signs of joint pain in German Shepherds include limping, stiffness, reluctance to move or jump, decreased activity, and signs of discomfort when touched. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your veterinarian for a thorough evaluation.
Can joint pain in German Shepherds be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent joint pain entirely, you can take steps to reduce the risk and manage symptoms. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight management, and early screening can help maintain joint health and prevent severe issues.
Are there specific exercises that are better for German Shepherds with joint pain?
Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and controlled play are ideal for German Shepherds with joint pain. Avoid high-impact activities like running on hard surfaces or repetitive jumping, as these can exacerbate joint issues.
What dietary supplements can help support joint health in German Shepherds?
Supplements containing glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids can support joint health in German Shepherds. These nutrients help maintain cartilage health, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function. Consult your veterinarian for specific supplement recommendations.
When should I consider surgical options for my German Shepherd’s joint pain?
Surgical options should be considered when non-surgical treatments are no longer effective in managing your dog’s joint pain and mobility issues. Your veterinarian can help determine if surgery is necessary and recommend the most appropriate procedure based on your dog’s condition.
Conclusion
Joint pain is a common concern for German Shepherds, but with proper care and attention, it can be managed effectively. By understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment options for joint pain, you can help ensure your German Shepherd leads a healthy, active, and fulfilling life. Regular veterinary check-ups, a balanced diet, appropriate exercise, and early intervention are key to maintaining your dog’s joint health. Remember to consult your veterinarian regularly to address any concerns and provide the best possible care for your beloved German Shepherd.